1. Introduction to QbTest
Objective
After this section the user should have a basic understanding of:
- What QbTest is
- What the different tasks are for the two different versions of QbTest
- What Regulatory bodies have approved QbTest
- What information can be gained from the QbTest report
QbTest
QbTest is a medical device that objectively measures cognitive performance and activity levels. QbTest combines a computer-administered Quantified Behavioural Task (QBT) with a high-resolution motion tracking system that uses an infrared camera to follow a reflective marker that is attached to a headband. The test objectively measures the three core signs of ADHD: hyperactivity, inattention, and impulsivity, to provide quantitative assessment of a patient’s activity level, ability to pay attention and inhibit impulses.
In addition to the Quantified Behavioural Test the patient performs an Ability Test that gives important information of the patient’s ability to manage the test situation.
The QbTest system consists of a computer, which displays the Continuous Performance Test, a response button, a headband with a reflective marker and an infrared high-resolution camera that records the reflective marker throughout the test. The test is available in two versions QbTest (6-12) and QbTest (12-60), depending on the patient’s age.
The test is CE-marked, registered by EMA (the European Medicine Agency) and cleared as a class II device by the FDA (US Food and Drug Administration). QbTest has been approved for use in both assessment, and to measure treatment effects, in patients aged between 6 and 60 years. All clinicians using QbTest must have completed a Qbtech approved training course and are required to attend regular refresher trainings to maintain a required standard of competency.
QbTest is not a stand-alone assessment, and the reports should always be interpreted within the wider clinical context and alongside other assessment procedures, for example, rating scales, classroom observations, developmental history, and clinical interview.

There are two age-differentiated versions of the QbTest. For both tasks, the patient is required to respond to a visual target stimulus on a screen by pressing a responder button as quickly and accurately as possible. The patient is also required to inhibit responses to stimuli on the screen defined as “Non-Targets”. In both test versions a stimulus is presented on the screen every two seconds.
The set-up and instructions for performing QbTest are strictly standardised in order to ensure that the patient is tested under the same conditions as the norm group whose scores they are compared to. Correct standardisation, as well as ensuring that the patient has understood and is able to perform the task, is essential to ensure the validity of the test and accuracy of the scores.
QbTest (6-12) version
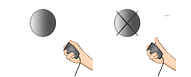 The task for QbTest (6-12), involves the rapid sequential presentation of either a grey circle, defined as a “Target”, which the patient should respond to by clicking the response button, or a grey circle with a cross over it, a “Non-Target”, to which the patient should inhibit his responses. In QbTest (6-12) a total of 450 stimuli are shown over 15 minutes, with an equal number of Targets and Non-targets.
The task for QbTest (6-12), involves the rapid sequential presentation of either a grey circle, defined as a “Target”, which the patient should respond to by clicking the response button, or a grey circle with a cross over it, a “Non-Target”, to which the patient should inhibit his responses. In QbTest (6-12) a total of 450 stimuli are shown over 15 minutes, with an equal number of Targets and Non-targets.
QbTest 12-60 version
 QbTest (12-60), presents a task with a slightly higher cognitive load and involves a rapid sequential presentation of one of four types of stimuli: a red square, a blue square, a red circle and a blue circle. In this version a stimulus is defined as a Target if it is identical in shape and colour to the stimulus immediately preceding it, and as a Non-target if it is not an identical match to the stimulus immediately preceding it. In this version of the test, 600 stimuli are shown over 20 minutes, with one stimulus being displayed every two seconds. There is a 25% Target to Non-Target ratio.
QbTest (12-60), presents a task with a slightly higher cognitive load and involves a rapid sequential presentation of one of four types of stimuli: a red square, a blue square, a red circle and a blue circle. In this version a stimulus is defined as a Target if it is identical in shape and colour to the stimulus immediately preceding it, and as a Non-target if it is not an identical match to the stimulus immediately preceding it. In this version of the test, 600 stimuli are shown over 20 minutes, with one stimulus being displayed every two seconds. There is a 25% Target to Non-Target ratio.
 The order of the Targets and Non-Targets in both test versions is semi-randomized to prevent practice effects in cases where the test is repeated.
The order of the Targets and Non-Targets in both test versions is semi-randomized to prevent practice effects in cases where the test is repeated.
QbTest result are displayed in clear reports
As soon as the test is finished, the results are automatically sent to our database for analysis against an age and sex matched norm group. The test results are presented as a clear report showing all three core symptom areas of ADHD, with both a visual and statistical analysis of the patient’s performance.

Summary:
- QbTest is an objective, computer-administered test, measuring all three core symptom domains of ADHD
- QbTest is a Class II Medical Device, is CE marked, approved by the EMA, and cleared by the FDA
- QbTest is a standardised assessment tool and can only be used by clinicians who have completed a Qbtech-approved training course
- Two versions with age adjusted tasks are available: QbTest (6-12) & QbTest (12-60)
- Clear reports give a visual presentation of attention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity symptoms, as well as statistical comparisons to age and sex matched normative groups
- QbTest is not a stand-alone tool. Reports should always be interpreted within the wider clinical context and alongside other assessment procedures (e.g. rating scales and clinical interviews). It is not a replacement for clinical judgement.
